The Guatemalan Sugar Industry ended the suar cane harvest and sugar production season driven by the CG02-163 sugarcane variety developed by scientists from the Guatemalan Center for Research and Training in Sugar Cane -Cengicaña-; this is a high-yield cane, resistant to diseases and adapted to climate variability.
 The CG02-163 sugarcane variety, currently occupying the largest planted area in the country, has a yield ranging from 11.5 to 12.5 tons of sugar per cultivated hectare. This variety produces an average of 1.4 tons more per hectare than the second-place variety CP72-2086, which comes from Canal Point in Florida, United States.
The CG02-163 sugarcane variety, currently occupying the largest planted area in the country, has a yield ranging from 11.5 to 12.5 tons of sugar per cultivated hectare. This variety produces an average of 1.4 tons more per hectare than the second-place variety CP72-2086, which comes from Canal Point in Florida, United States.
This contributed to the production for the 2020/2021 harvest being 55,758,979 quintals of sugar or 2,564,901 metric tons of sugar, with a cultivated area of 253 thousand hectares. This harvest was challenging due to the conditions presented by the pandemic and all the biosanitary measures were taken for the prevention of COVID-19, both in the workplace and in the communities of the South of Guatemala.
“Research and development is a fundamental pillar for the Sugar Industry, it has contributed to improve efficiency each harvest and has allowed us to be more competitive worldwide. The development of cane varieties is one of the great contributions of the research center, until this year we have developed, through the natural crossing of plants, 33 Guatemalan cane varieties that are more productive, resistant to pests and climate change”, commented Luis Miguel Paiz, general manager of the Guatemalan Sugar Producers Association -Asazgua-.
Renewable energy cogeneration
As part of the research, sugarcane residues are also used to produce alcohol and the generation of renewable energy and during the 2020/2021 harvest, cogeneration mills contributed with 30% of the energy consumed in the country, reaching peaks in some days that reached 46%.
 In that period, the Sugar Industry generated 1,844 (GWh) gigawatt-hours of renewable energy to deliver to the grid; the equivalent of 2 times the consumption of all the Municipal Electric Companies of Guatemala for 1 year.
In that period, the Sugar Industry generated 1,844 (GWh) gigawatt-hours of renewable energy to deliver to the grid; the equivalent of 2 times the consumption of all the Municipal Electric Companies of Guatemala for 1 year.
Zafra is development for Guatemala
The zafra begins in November and ends in May of the following year and, for the South of Guatemala, it is a season of economic reactivation since it generates more than 54 thousand direct jobs and the hiring of more than 6,325 suppliers, large, medium and small of products and services, who also become employers and multiply opportunities for the local population. The sugar sector generates more than 270 thousand indirect jobs each year.
 The sugar mills associated with Asazgua operate under a strict labor and environmental policy and distribute each year around US$402 million in wages and salaries, in addition to providing complementary health services to their collaborators. In a study prepared by Asazgua, the economic footprint or spill of sugar in Guatemala is more than US$ 1,188 million and reaches 90% of the country’s municipalities.
The sugar mills associated with Asazgua operate under a strict labor and environmental policy and distribute each year around US$402 million in wages and salaries, in addition to providing complementary health services to their collaborators. In a study prepared by Asazgua, the economic footprint or spill of sugar in Guatemala is more than US$ 1,188 million and reaches 90% of the country’s municipalities.

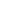

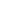




 The hydraulic bridges, sugar launchers, automatic samplers, conveyor belt system, shipping cranes, among others, were designed and manufactured in Guatemala with the support of the Sugar Industry.
The hydraulic bridges, sugar launchers, automatic samplers, conveyor belt system, shipping cranes, among others, were designed and manufactured in Guatemala with the support of the Sugar Industry.

 Since the beginning of the pandemic, the Guatemalan Sugar Industry has distributed
Since the beginning of the pandemic, the Guatemalan Sugar Industry has distributed 