The Guatemalan Sugar Association and the Private Institute for Climate Change Research -ICC- presented the 2023 Reforestation Plan, which this year consists of planting more than 955,000 trees in 11 departments of the country that will cover around 860 hectares of land, a space that is equivalent to about 1,229 soccer fields.
With the first reforestation day, of the season, the 2023 Reforestation Plan began. The activity, in which 500 trees were planted, took place at the Limones farm at the outskirts of the town Santa Lucía Cotzumalguapa; located at 90 kilometers (56 miles) at the south of Guatemala city.
The event included the participation of Alfredo Vila, president of the Association of Sugar Producers of Guatemala -Asazgua-; Dr. Alex Guerra, Director of the Private Institute for Climate Change Research -ICC-; Ing. Rony Granados, Manager of the National Institute of Forests -INAB-; as well as collaborators of the sugar mills and journalists from the media.
“With this year’s reforestation plan, 8.8 million trees will be planted since 2011, in strategic areas for the recovery and conservation of basins that influence the South of Guatemala. This as part of the commitment of the Sugarcane Agroindustry to sustainability and the care of natural resources,” said Alfredo Vila, president of Asazgua.

Reforestation will take place in 11 departments of the country: Escuintla, Chimaltenango, Retalhuleu, Suchitepéquez, Sacatepéquez, Santa Rosa, Jalapa, Quetzaltenango, Sololá, Jutiapa and San Marcos.
“In 2011 Asazgua, ICC and local partners started a program for the conservation and recovery of forests in strategic areas to contribute to the protection of riverbanks, water recharge zones and biological corridors. Around 7,000 hectares have been reforested, to which 860 will be added this year. By the end of 2023, the equivalent of 11,000 soccer fields will have been reforested,” said Alex Guerra, Director of the ICC.
Since the beginning of the program in 2011, 55 native species have been reforested, among them: matilisguate, aripín, cenícero, madre cacao, conacaste, cedar, mahogany, palo blanco, volador, plumillo, hormigo, caulote, among others.
ICC technical support
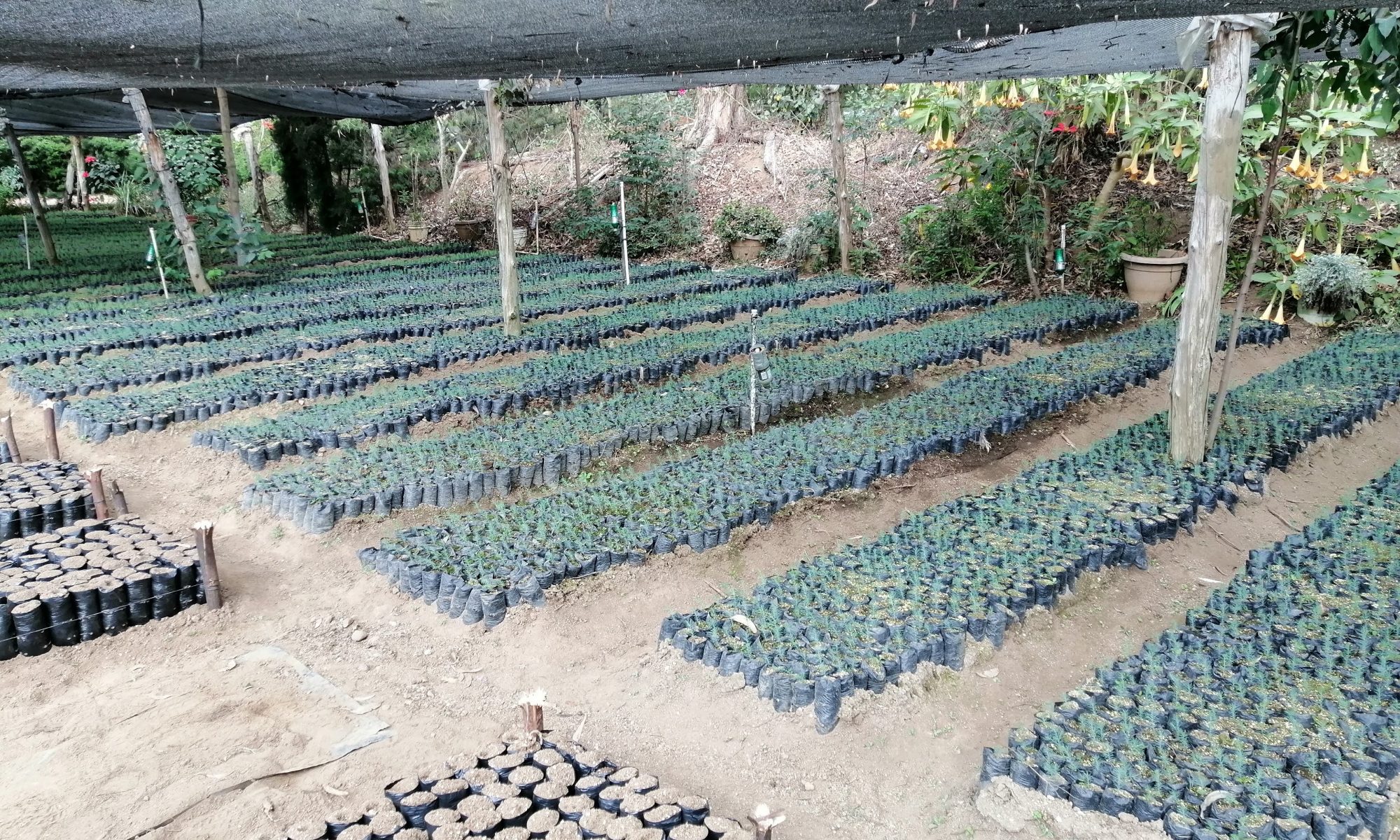
The ICC provides support and technical and scientific advice and is the link with communities, organizations, municipal and regional authorities, for the installation of nurseries and identification of reforestation areas. The 955,000 plants that will be planted this year were produced in 67 nurseries installed in different locations. In addition, this program has the support of the National Institute of Forests -INAB-.
In addition to this effort, the sugar mills have individual reforestation programs and their own natural forests, through which they total 14,800 hectares, equivalent to 21,144 soccer fields.

These efforts and those that are planned, contribute to the management of the Guatemalan Pacific basins since forest resources are vital to maintain the water cycle, protect the soil, maintain the diversity of flora and fauna, among other benefits.
Reforestation is also part of the contributions of the Sugarcane Agroindustry to the Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations Organization, especially goal 15: “Life of Terrestrial Ecosystems”, which aims to manage forests of sustainable manner and objective 13 “Climate Action” which implies actions to combat the effects of climate change.
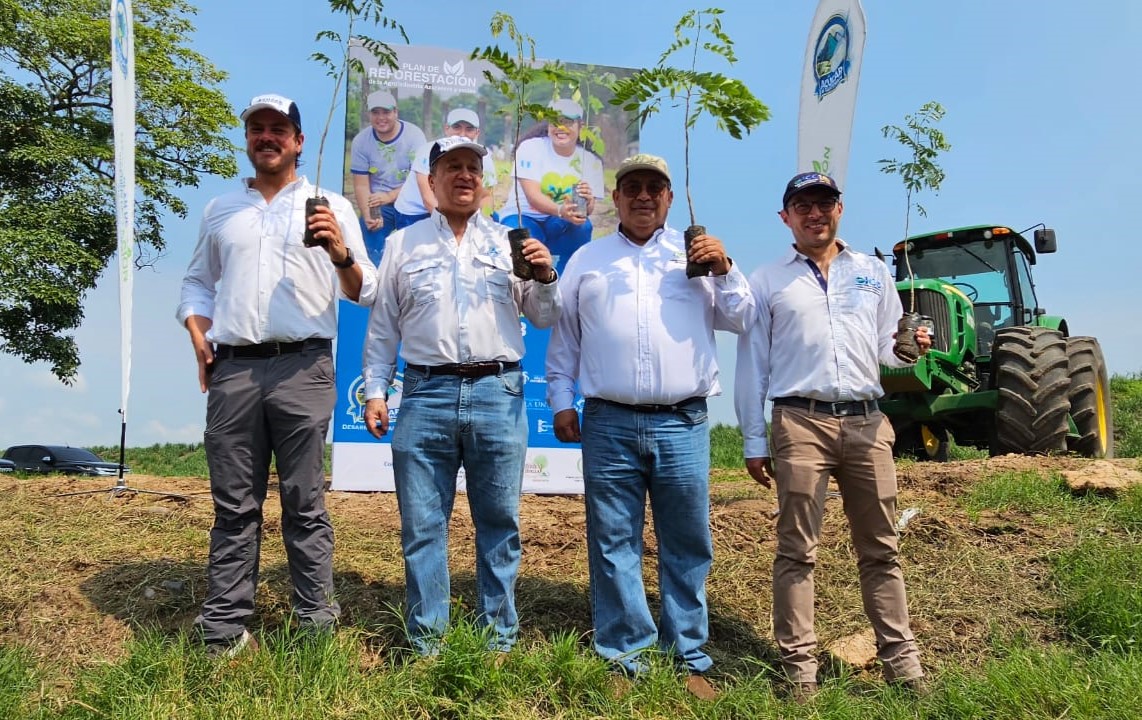

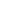

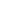







 The Reforestation Plan began with the planting of 300 trees on a farm Called Belem, jurisdiction of Masagua, Escuintla, located at 370 kilometers (230 miles) in the south of Guatemala City. With this activity, the reforestation season officially begins, and will last until August.
The Reforestation Plan began with the planting of 300 trees on a farm Called Belem, jurisdiction of Masagua, Escuintla, located at 370 kilometers (230 miles) in the south of Guatemala City. With this activity, the reforestation season officially begins, and will last until August.
 The members of the Ocosito Technical Committee; included the Guatemalan Sugar Industry have promoted a program for the restoration and conservation of the basin through reforestation for the creation of
The members of the Ocosito Technical Committee; included the Guatemalan Sugar Industry have promoted a program for the restoration and conservation of the basin through reforestation for the creation of  The technical committee was born in 2016 out of the need to organize and make rational use of water. In 2021, promoted by the Vice Ministry of Water, through Government Agreement 19-2021, it was institutionalized as a more comprehensive technical organization for the recovery and conservation of the Ocosito basin.
The technical committee was born in 2016 out of the need to organize and make rational use of water. In 2021, promoted by the Vice Ministry of Water, through Government Agreement 19-2021, it was institutionalized as a more comprehensive technical organization for the recovery and conservation of the Ocosito basin.
 The nurseries in which the trees are prepared for the National Reforestation Plan are managed by municipalities, institutions, companies, and communities. These inter-institutional alliances help to promote forest culture in the communities where they are implemented.
The nurseries in which the trees are prepared for the National Reforestation Plan are managed by municipalities, institutions, companies, and communities. These inter-institutional alliances help to promote forest culture in the communities where they are implemented.









