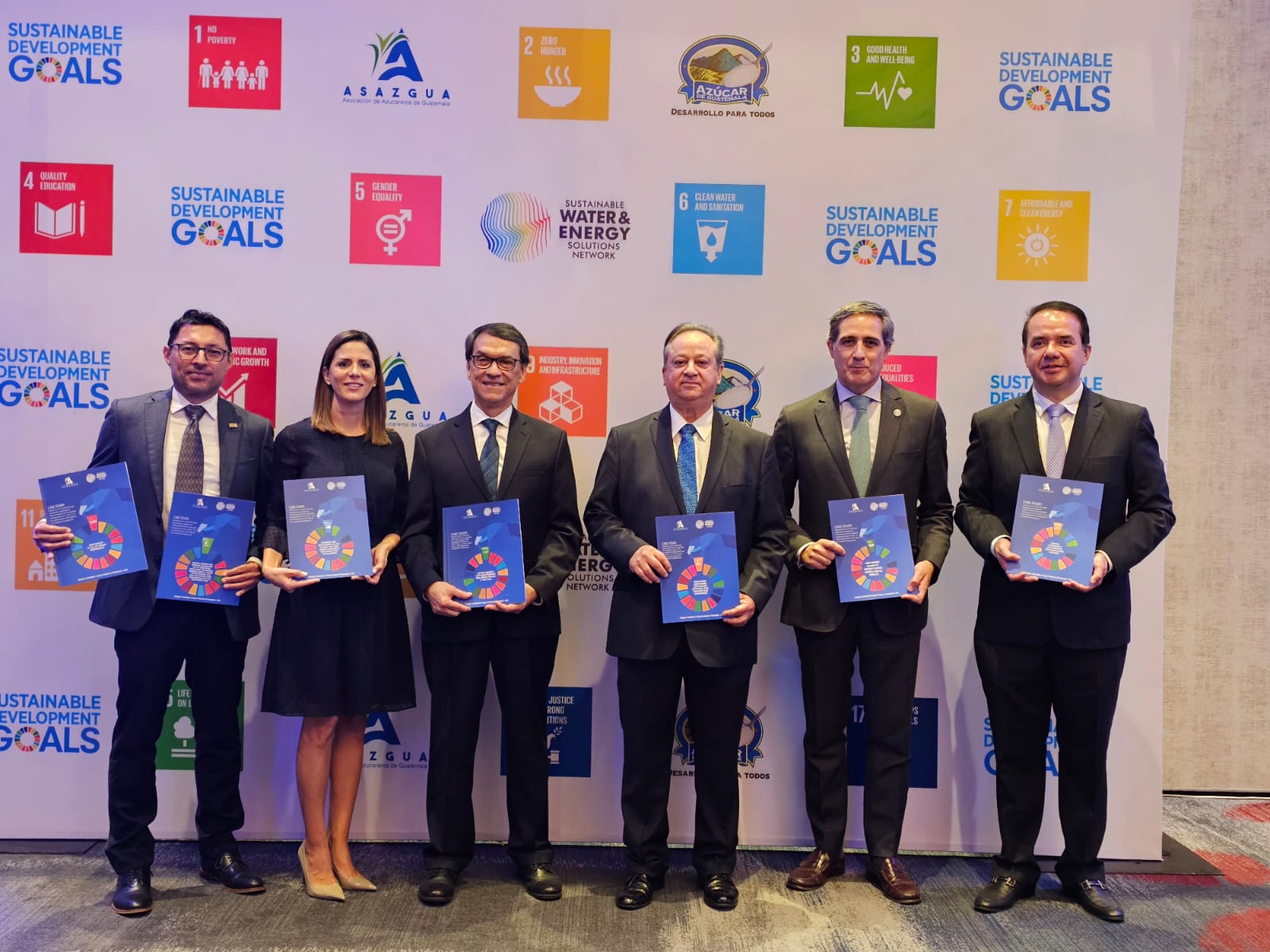
The Sugar Industry, in addition to being an economic engine for Guatemala, is an ally of sustainable development and there are various initiatives and projects in the environmental, social, and economic areas, through which the sector supports compliance with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), of the United Nations Organization (UN) and this Thursday, the Guatemalan Sugar Producers Association (Asazgua) presented the Case Studies that detail these contributions.
The event was attended by Mr. Ivan Vera, UN Senior Consultant; Alfredo Vila, President of Asazgua; Luis Miguel Paiz, General Manager of Asazgua; Mr. Ricardo Rapallo, Ad Interim Resident Coordinator of the United Nations in Guatemala; as well as representatives of the diplomatic corps, public officials, and managers of Asazgua.
“Our sector is a key actor in the development of the country and therefore our responsibility is also great. We understand our role as generators of opportunities and prosperity for millions of people in Guatemala,

but we also assume the responsibility of doing so by generating decent employment, promoting development in communities, taking advantage of and using natural resources in a sustainable manner, and for this we have implemented concrete actions, such as precision agriculture techniques, use and development of technologies in our processes, water reuse, renewable energy generation, among others”, commented Alfredo Vila, president of Asazgua.
The SDGs were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a universal call to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity.

The Guatemalan Sugar Industry, as a member of the United Nations Network for Sustainable Solutions in Water and Energy, presented 17 case studies on the contributions of the sector to the fulfillment of the Sustainable Development Goals, as well as the Guild Sustainability Report under the GRI methodology.
SDG compliance economic axis:
- Each year more than 55,000 direct jobs and 278,000 indirect jobs are generated in dignified and decent conditions. The value chain of the Sugar Industry reaches more than 6,000 companies -small, medium and large-, which are suppliers of goods and services, which in turn generate opportunities for thousands of families.
- The economic footprint of Sugar in Guatemala is USD1,568 million per year, this economic benefit reaches 90% of the country’s municipalities. Every year USD375 million are distributed in wages and salaries.
- Guatemala is the third largest sugar producer in Latin America, and the sixth worldwide. It also ranks third in productivity of tons of sugar per hectare globally.
- The products of the sugar industry represent the second place of agro-industrial exports in the country.
- The sugarcane bagasse or the biomass that remains after the juice is extracted to produce sugar, is used for the generation of renewable energy and contributes to the national interconnected system around 30% of the electricity that the country consumes during the Zafra.
SDG compliance social axis:
- The Sugar Foundation -Fundazucar-promotes social programs focused on the areas of health, education, and municipal strengthening, through a self-management model that promotes the empowerment and citizen participation of women, youth, teachers, health professionals, community leaders and local authorities.
- Through the Better Families program, Food and Nutrition Security, self-esteem, self-management, and leadership are promoted in women as agents of change for the development and well-being of their families.
- The Health Comes First program trains health professionals at the first level of care in the municipalities of the South of Guatemala to develop technical skills with the purpose of improving service and promoting preventive health.
- Through the Fundazucar medical clinics, access to healthcare is facilitated for thousands of people in the south of the country.
- Since 1976, the fortification of sugar with Vitamin A has been essential to combat childhood blindness caused by deficiency of this micronutrient.
- Study opportunities are provided for young people between the ages of 15 and 25 so that they can study in technical or university careers. The goal of these scholarships is to provide them with opportunities to lift themselves out of poverty.
SDG compliance environmental axis:
- The sugar industry has invested in research and development with the Guatemalan Sugar Cane Research Center -Cengicaña-, which among its main functions is the development and promotion of good practices for cane cultivation, sugar production and other by-products, as well as the promotion of precision agriculture and crop adaptation to climate variability.
- The Water Footprint of Guatemalan sugarcane producers is 45% lower than the world average, according to the study of the Water Footprint of sugarcane.
- In a joint effort between ICC, community members, local authorities, and the sugar sector, since 2010 the program for the recovery and conservation of forests in the basins of the Pacific slope has been carried out. 7.7 million trees have been produced, which contributes to water recharge, biodiversity, among other functions for flora and fauna.
- The Sugar Industry actively participates in technical water tables on the south of Guatemala with communities, local authorities, government institutions, human rights organizations, and other agricultural producers, for the coordinated and responsible use of river water. It is a unique organizational model in the country.
- Cengicaña scientists developed the Cengiriegos application, which allows the crop to apply only the amount of water it needs, depending on the type of soil, the age of the plant and the climatic conditions.
- Use of water recirculation systems in factories for its reuse and optimization.
For more information you can access all the case studies here.